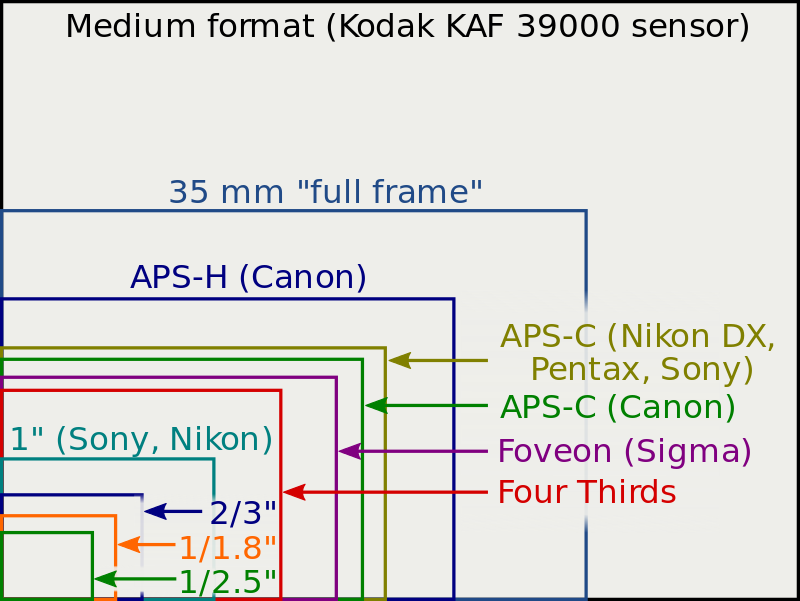
Aps C Vs Cmos refer to two different aspects of digital imaging sensors. APS-C denotes a sensor size smaller than full-frame, while CMOS stands for a type of digital image sensor technology.
Selecting between an APS-C and a CMOS sensor requires understanding their roles in photography. APS-C sensors, typically found in many DSLRs and mirrorless cameras, offer a balance between cost, size, and image quality. They have a crop factor that affects the field of view, narrowing it compared to full-frame sensors.
CMOS, or Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor, is a technology used in the majority of digital cameras to convert light into electrons. Digital cameras widely utilize CMOS sensors for their efficiency and lower power consumption. Manufacturers often combine the APS-C size with CMOS technology to create high-quality, yet affordable imaging devices perfect for both enthusiasts and professional photographers. This balanced approach ensures sharp images with reduced noise levels, even in lower light conditions. Deciphering between the sizes and tech types enhances your photography toolkit choices, improving your shot’s outcome with the knowledge of each sensor’s capabilities.
Aps-c Explained
APS-C sensors are a staple in many digital cameras. Common in both DSLRs and mirrorless systems, these sensors offer a balance between performance and size. They are smaller than full-frame sensors but larger than the micro four-thirds system. APS-C stands for Advanced Photo System type-C, which has its own unique set of advantages for photographers.
The evolution of APS-C sensors
The Evolution Of Aps-c Sensors
The journey of APS-C sensors began in the film era. They were once part of the Advanced Photo System format designed for ease of use. With the digital revolution, these sensors reemerged. They now suit high-end consumer cameras. Advancements in technology have sharpened their image quality. This rivals professional gear.
- 1996: Introduction with the Advanced Photo System
- Early 2000s: Transition to digital format
- Present: Continuous improvements in technology
Characteristics of APS-C sized sensors
Characteristics Of Aps-c Sized Sensors
Many traits make APS-C sized sensors popular. They include excellent image quality and a more compact design compared to full-frame cameras.
- Crop Factor: Generally 1.5x to 1.6x compared to full frame
- Resolution: Ranging from 16 to 32 megapixels
- Low-Light Performance: Not as good as full-frame but improving steadily
- Depth of Field: Higher in APS-C than full-frame, beneficial for some photography styles
- Cost: Usually more affordable than full-frame systems
Credit: en.wikipedia.org
Cmos Technology Unveiled
Understanding sensors is key to unlocking camera potential. The heart of digital photography beats with CMOS sensor technology. Let’s explore the brilliance behind these sensors that capture life’s moments in stunning clarity.
Basics Of Cmos Sensor Technology
CMOS stands for Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor. This technology is crucial in capturing images within digital cameras. CMOS sensors convert light into electrons. These tiny building blocks form the images we see.
Let’s break down the process:
- Light hits the sensor.
- The sensor turns light into an electric signal.
- Each pixel on the sensor adds to the final image.
These steps all happen at incredible speeds. That is why we can capture moments as they happen.
Advantages Of Cmos Sensors In Modern Photography
CMOS sensors bring many benefits to photographers. From beginners to pros, all can enjoy these perks:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Low Power Consumption | CMOS sensors use less battery. Your camera lasts longer on a single charge. |
| High-Speed Processing | They handle lots of data fast. This means quick photo capture and video recording. |
| Versatility | These sensors are great for all kinds of cameras, from phones to high-end DSLRs. |
| Cost-Effectiveness | CMOS technology is easier on the wallet without sacrificing quality. |
These attributes make CMOS the go-to for modern photography. They ensure sharp, vibrant photos every time.
Comparing Aps-c And Cmos
Welcome to our deep-dive looking at two common sensor types in digital photography: APS-C and CMOS. Understanding the differences between these sensors can help photographers make informed choices about their equipment. Let’s compare these technologies focusing on sensor size, image quality, and performance in various lighting conditions.
Sensor Size And Image Quality
APS-C sensors are smaller than full-frame sensors but larger than most compact camera sensors. This size impacts the image quality.
- Greater depth of field control
- Good balance between size and quality
- Less noise at higher ISOs compared to smaller sensors
On the other hand, CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) is a type of sensor technology used in both APS-C and full-frame cameras. It refers to the way the sensor captures light and converts it to digital data.
| CMOS Sensor Advantage | Details |
|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | Uses less power, extending battery life |
| Fast Processing Speed | Allows quick image capture and video recording |
| High Dynamic Range | Capable of capturing a wide range of light and dark tones |
Performance In Varied Lighting Conditions
In diverse lighting, sensor size plays a pivotal role in image performance. Larger APS-C sensors often fare better than smaller counterparts.
Higher ISO capabilities mean APS-C sensors maintain quality in low light. Noise is more controlled, preserving details.
CMOS sensors, irrespective of size, are designed for efficiency in light capture. This results in better low-light performance compared to older CCD sensors.
- Improved light sensitivity
- Lower noise ratios at higher ISOs
- Capability to handle contrasting light situations
Impact On Camera Performance

When comparing APS-C and CMOS sensors, camera performance often becomes a hot topic of discussion.
APS-C sensors are smaller than full-frame CMOS sensors.
This size difference can have a dramatic effect on how a camera captures images.
Let’s delve into two crucial aspects: autofocus (AF) speed and accuracy, and continuous shooting capabilities.
Autofocus Speed And Accuracy
Autofocus speed is how quickly your camera can focus.
Accuracy makes sure it’s sharp.
APS-C cameras often have quick autofocus.
Many sport advanced AF systems tuned for speed.
CMOS sensors, particularly those in full-frame bodies, are capable of precise AF in varied lighting.
They use advanced focusing technologies like phase detection.
Here are some keypoints:
- APS-C has quick AF, great for action shots.
- CMOS shines in AF precision, even in low light.
Continuous Shooting Capabilities
Continuous shooting lets you take lots of photos quickly. It’s measured in frames per second (fps).
Cameras with an APS-C sensor can be nimble. They often offer high fps rates.
APS-C is ideal for shooting sports or wildlife.
The CMOS full-frame sensors may have lower fps.
But their image quality is usually top-notch.
A big sensor can gather more light. This makes each image clearer and more detailed.
Look at this comparison:
| Sensor Type | Continuous Shooting Speed |
|---|---|
| APS-C | Fast (e.g., 10-20 fps) |
| CMOS Full-Frame | Slower but High Quality (e.g., 5-10 fps) |
Choosing The Right Sensor For Your Needs
When choosing the right sensor for your camera, two popular options come to mind: APS-C and CMOS. Each sensor has unique strengths. It’s vital to know which one fits your specific photo-taking needs. Let’s dive into the factors to consider.
Considering The Type Of Photography
Your preferred photography style plays a big role in sensor selection. APS-C sensors work great for general use. They provide a good balance between size and quality. Wildlife and sports photographers love the extra reach provided by the APS-C’s crop factor. On the other hand, CMOS sensors are often full-frame and excellent in low light. They suit professional portrait and landscape photographers well.
Choose APS-C for:
- Increased depth of field
- Extended zoom range
- Budget-friendly lenses
Choose CMOS for:
- Superior low light performance
- Higher dynamic range
- Professional image quality
Budget And Camera System Compatibility
Budget constraints are real. Cost-effective photography often means choosing an APS-C sensor. Cameras with APS-C sensors are usually less expensive. They make high-quality photography accessible to more people. Checking compatibility with your existing lenses and accessories is key. Make sure the sensor you pick works with your gear.
Consider the following for budgeting:
| Factor | APS-C | CMOS |
|---|---|---|
| Initial camera cost | Lower | Higher |
| Lens costs | Generally lower | Varies, often higher |
| Performance-to-price ratio | Excellent | Depends on model |
Weighing your needs against your budget will help ensure you invest in the right sensor-equipped camera.
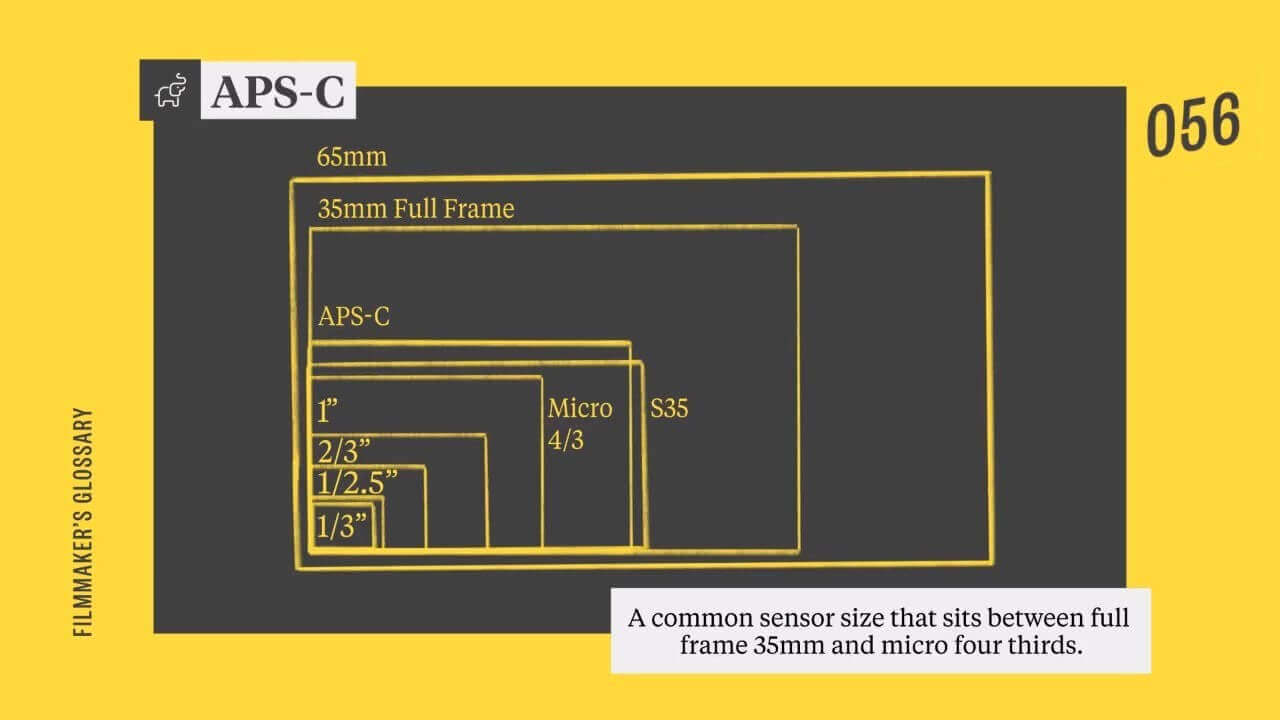
Credit: www.studiobinder.com
Frequently Asked Questions For Aps C Vs Cmos
What Is Aps-c In Camera Sensors?
APS-C stands for “Advanced Photo System type-C,” a sensor size frequently used in many digital cameras. It’s smaller than a full-frame sensor but provides a balance between image quality and camera portability, making it popular in consumer-grade DSLRs and mirrorless cameras.
How Does Aps-c Compare To Full-frame Sensors?
APS-C sensors are smaller than full-frame sensors, resulting in a crop factor that affects the lens’s effective focal length. Images are typically more zoomed in compared to full-frame. APS-C offers less depth of field and light gathering but is more affordable and compact.
What Does Cmos Mean In Camera Technology?
CMOS stands for “Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor. ” It’s a type of image sensor used in digital cameras that converts light into electronic signals. CMOS technology allows for lower power consumption, faster processing speeds, and integration of more functions on a single chip.
Which Is Better For Photography, Aps-c Or Cmos?
APS-C and CMOS are not directly comparable; APS-C refers to sensor size, while CMOS is a type of image sensor technology. Many APS-C sensors are based on CMOS technology. The choice between sensor sizes depends on the specific photographic needs and preferences.
In Conclusion:
Choosing between APS-C and CMOS sensors involves personal and professional considerations. It’s crucial for photographers to weigh sensor size, image quality, and the type of shooting they’ll be doing. Whatever your choice, ensure it amplifies your creative vision and meets your photography demands.
Embrace the sensor that aligns with your artistic journey and capture the world as you see it.